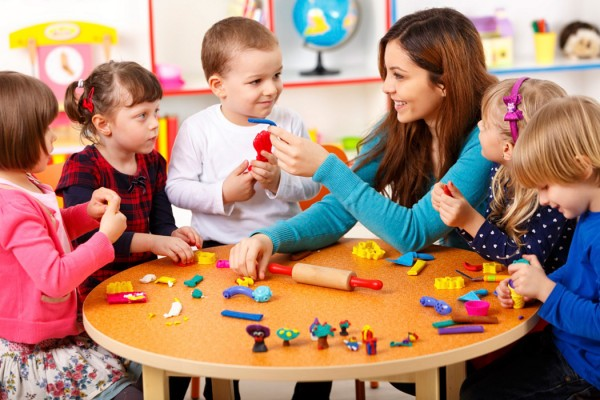
Childcare for working mothers has become a pivotal topic, especially as women continue to make strides toward gender equity in the workforce. With recent insights from acclaimed economist Claudia Goldin, we see that the historical context of federally funded childcare offers vital lessons for today’s working mothers. Goldin’s research highlights the potential impacts of the Lanham Act, a policy that once provided critical support for childcare programs during World War II, showing how such initiatives can effectively empower women and enhance their professional contributions. The study reveals that while the act was designed primarily to bolster the workforce, it also created essential resources for mothers striving to balance career aspirations with childcare responsibilities. Understanding the legacy of these programs sheds light on the ongoing challenges and opportunities faced by women in the workforce today, making it clear that effective childcare solutions are crucial for advancing gender equity.
For mothers balancing jobs and family life, finding reliable childcare options is essential. The historical framework of childcare support during wartime demonstrates the significant role that community and governmental aid can play in enabling women to pursue careers while raising children. Goldin’s research on early childcare initiatives illustrates how structured programs can alleviate pressure on working moms, fostering a better work-life equilibrium. Alternative solutions for childcare accessibility resonate deeply today as businesses strive to accommodate the needs of working parents, ensuring that they do not have to choose between professional advancement and family care. As discussions around women in the workforce evolve, it is imperative to consider multifaceted childcare solutions, which could reshape the future for mothers and their children.
Understanding the Lanham Act and Its Impact on Childcare
The Lanham Act, introduced during World War II, was primarily aimed at addressing labor shortages by supporting the employment of mothers through federally funded childcare. This initiative was pivotal in changing societal views about working women, allowing them to enter the workforce with the support they needed for their young children. Claudia Goldin, a prominent economic historian, highlights how this program effectively created a safety net for mothers, enabling them to balance work and family responsibilities during a crucial time when national productivity was essential.
Goldin’s research indicates that the Lanham Act not only established a system of childcare centers across the United States but also emphasized the importance of women in the labor market. By offering facilities that catered to the needs of working mothers, the act played a critical role in shifting public sentiment towards women in the workforce. The data reveal that these nurseries were strategically placed in communities where women were already engaged in various industries, thus reinforcing the connection between accessible childcare and female employment.
The Role of Federally Funded Childcare in Supporting Working Mothers
Federally funded childcare has proven to be a significant factor in supporting working mothers, allowing them to pursue career opportunities without compromising their children’s well-being. Programs like those founded under the Lanham Act are rare but illustrate the power of governmental support in enhancing workforce participation. By implementing policies that provide affordable childcare options, the government can alleviate many obstacles mothers face, especially in times of economic uncertainty.
Furthermore, the long-standing challenges in the labor market for women underscore the necessity of effective childcare programs. As women increasingly enter various professional fields, having access to reliable childcare is essential for maintaining job continuity and advancing in their careers. Goldin’s analysis suggests that when mothers have access to appropriate childcare, they are more likely to remain in the workforce, thereby contributing to overall economic growth.
Claudia Goldin’s Insights into Women in the Workforce
Claudia Goldin, renowned for her contributions to economic history, provides a comprehensive look at the evolution of women’s roles in the workforce. She emphasizes that the development of childcare support mechanisms, like those established by the Lanham Act, has historically been crucial in enabling women to pursue careers amidst societal constraints. Goldin’s work sheds light on how such programs have historically benefitted not just individual families but also the economy at large.
In her research, Goldin posits that the participation of women in the labor market is contingent upon supportive structures like childcare. The Lanham Act, despite its limited duration, serves as a model for contemporary discussions around family-friendly workplace policies. By addressing the history of women’s labor roles, Goldin highlights both the progress made and the ongoing challenges that still require attention today.
Evaluating Historical Childcare Programs and Their Legacy
The legacy of historical childcare programs such as those under the Lanham Act provides valuable lessons for current and future childcare initiatives. It demonstrates how government intervention can lead to significant enhancements in women’s workforce participation, thus impacting economic conditions. By studying past efforts, contemporary policymakers can identify effective strategies to support working mothers through improved childcare solutions.
Moreover, the importance of these programs extends beyond just immediate benefits; they lay the groundwork for societal transformations regarding attitudes towards working mothers. Goldin’s investigation into these historical precedents reveals a pattern where supportive childcare is linked to increased female labor participation, which can inspire current debates about the need for comprehensive childcare frameworks today.
Childcare Programs: A Necessity for Economic Recovery
In the wake of economic downturns, childcare programs have often been overlooked, yet they are critical for promoting recovery. Investment in federally funded childcare not only supports families but also stimulates job growth and economic activity. Goldin’s analysis outlines how robust childcare frameworks can serve as a catalyst in rejuvenating the workforce, particularly in sectors heavily reliant on female labor.
As we navigate the complexities of modern economies, the necessity for effective childcare systems becomes increasingly apparent. By ensuring that working mothers have reliable care for their children, the economy can benefit from the full engagement of this demographic, showcasing how essential childcare systems are to economic stability and growth.
The Intersection of Gender Equity and Childcare Services
The provision of childcare services is inherently tied to the broader conversation on gender equity. Programs designed to support working mothers, such as those initiated by the Lanham Act, play a crucial role in leveling the playing field for women in the workforce. Goldin asserts that equitable access to childcare is foundational in addressing the persistent wage gaps and employment disparities experienced by mothers today.
Furthermore, gender equity in the workplace cannot be achieved without addressing the need for comprehensive childcare services. The historical context provided by Goldin illustrates that when women are given the means to balance work and family, they can thrive professionally and contribute to economic prosperity. This intersectionality highlights the importance of continued advocacy for family-oriented policies in the modern economy.
Reviving Support for Childcare Initiatives Today
In light of the lessons learned from the Lanham Act, there is an urgent need to revive support for childcare initiatives. Recent research indicates that accessible childcare remains a pressing concern for working mothers and families at large. By drawing parallels with historical programs, current advocates can make a compelling case for renewed federal investment in childcare as a means to bolster the workforce and promote family health.
Advocating for the revival of childcare programs means recognizing the modern needs of families and the evolving nature of work. Investing in childcare services today can significantly uplift the workforce by allowing mothers to engage fully in their professional lives. This revival could lead to sustainable economic growth, echoing the important role that childcare has played in the past.
Childcare Funding and Its Economic Implications
The implications of childcare funding extend far beyond immediate assistance to families; they have profound economic repercussions. Investment in childcare programs is often tied to enhanced workforce participation, leading to greater productivity and consumer spending. Goldin’s findings underline the notion that strategic funding of childcare services can yield long-term economic benefits, positing childcare as a vital infrastructure not just for families but for the entire economy.
Moreover, as workforce dynamics change and more women enter various sectors, the necessity for reliable childcare systems grows more significant. Policymakers must recognize that without adequate funding for childcare, we risk losing out on the potential contributions of women to the economy, especially in critical recovery phases. The economic implications of neglecting childcare are far-reaching, necessitating immediate attention from both the public and private sectors.
Exploring Future Directions for Childcare Policies
Looking ahead, the exploration of future directions for childcare policies must be informed by historical precedents such as the Lanham Act. Policymakers should consider how to establish robust childcare systems that address the needs of modern families while promoting women’s equality in the workplace. As Goldin’s research suggests, understanding the past can provide invaluable insights into designing forward-thinking policies that resonate with today’s economic landscape.
Future childcare policies should also emphasize inclusivity, ensuring that all working mothers, regardless of their socio-economic status, have access to affordable childcare solutions. This aligns with ongoing discussions around gender equity and economic sustainability, creating pathways for women to thrive in the workforce while raising families. Through collaborative efforts, we can build a future where childcare is recognized as a fundamental component of our economic infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role did federally funded childcare play for working mothers during World War II?
Federally funded childcare, particularly through the Lanham Act, provided crucial support for working mothers during World War II by creating nurseries that allowed them to enter and remain in the workforce. This program aimed to mobilize mothers to contribute to the war effort, offering supervised care and education for their children.
How does Claudia Goldin’s research highlight the importance of childcare for working mothers?
Claudia Goldin’s research emphasizes that effective childcare support, such as that provided through the Lanham Act, is vital for increasing women’s participation in the workforce. Her findings reveal that when working mothers have access to quality childcare, they can pursue higher-wage jobs and contribute significantly to the economy.
What impact did the Lanham Act have on childcare programs for working mothers?
The Lanham Act led to the establishment of federally funded childcare programs which included nurseries and extended care services for working mothers. This historically significant act supported the workforce by enabling mothers to balance their family responsibilities while contributing to critical industries during the war.
Why is the discussion of women in the workforce and childcare for working mothers relevant today?
The discussion remains relevant as current debates about gender equity in the workplace continue to highlight the necessity for accessible childcare options. Understanding the historical context provided by programs like those established under the Lanham Act can help shape current policies aimed at supporting working mothers in their careers.
What lessons can modern society learn from the childcare initiatives of the Lanham Act for working mothers?
The Lanham Act showed that robustly funded childcare initiatives can significantly improve women’s employment rates and economic independence. Today, implementing similar federally funded childcare programs could empower modern working mothers, supporting their workforce participation and enhancing family well-being.
In what ways did the childcare programs from the Lanham Act differ from those that exist today?
Childcare programs established under the Lanham Act were nationally funded and accessible to a broader demographic of working mothers, unlike many current programs which often target low-income families exclusively. This difference highlights the potential benefits of universal childcare access in enhancing women’s workforce participation.
How does the historical context of childcare for working mothers inform current childcare policy debates?
Historical insights from the Lanham Act reveal that comprehensive, federally funded childcare support can have transformative effects on women’s employment and economic status. This context is crucial for informing current childcare policy debates, advocating for more inclusive and effective solutions for working mothers.
What challenges did working mothers face regarding childcare during the era of the Lanham Act?
Despite the establishment of nurseries, working mothers faced societal stigma and opposition regarding their dual roles. Many believed women should not work while having preschool-aged children, which presents a continuing challenge for modern working mothers today in achieving workplace equality.
How can further research build upon Claudia Goldin’s findings about working mothers and childcare?
Future research can delve deeper into the long-term effects of federally funded childcare programs like the Lanham Act on children as they mature, and how such initiatives could inform current policies to better support working mothers in the workforce.
What is the significance of federally funded childcare programs in supporting women in the workforce today?
Federally funded childcare programs are crucial for supporting women in the workforce by providing the necessary resources and support that allow them to balance work and family responsibilities, thus promoting economic equality and workforce participation.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Lanham Act Introduction | Analyzed by Claudia Goldin, aimed to support working mothers during WWII. |
| Creation of Nurseries | Funded nurseries for preschool children; intended to support labor during the war. |
| Federal Funding | Allocated nearly $52 million for nurseries between 1943-46 to help working mothers. |
| Economic Impact | Increased employment levels as mothers entered the workforce, despite negative public sentiment. |
| Target Demographic | Focused on working mothers with children aged 2 to 11, rather than low-income families. |
| Labor Force Expansion | Though it increased labor participation, much of the benefit was for women already employed. |
| Historical Significance | Serves as a precedent for discussions on childcare policies and support for working mothers today. |
Summary
Childcare for working mothers is pivotal for balancing work and family responsibilities, a discussion that dates back to significant historical legislation like the Lanham Act during WWII. This act not only provided vital childcare support for women entering the workforce but also underscored the importance of accessible childcare services in enhancing economic participation. As modern working mothers continue to seek equitable solutions, the lessons gleaned from the past highlight the need for sustained advocacy and policy development to ensure that childcare remains a priority, facilitating a more supportive environment for working families.