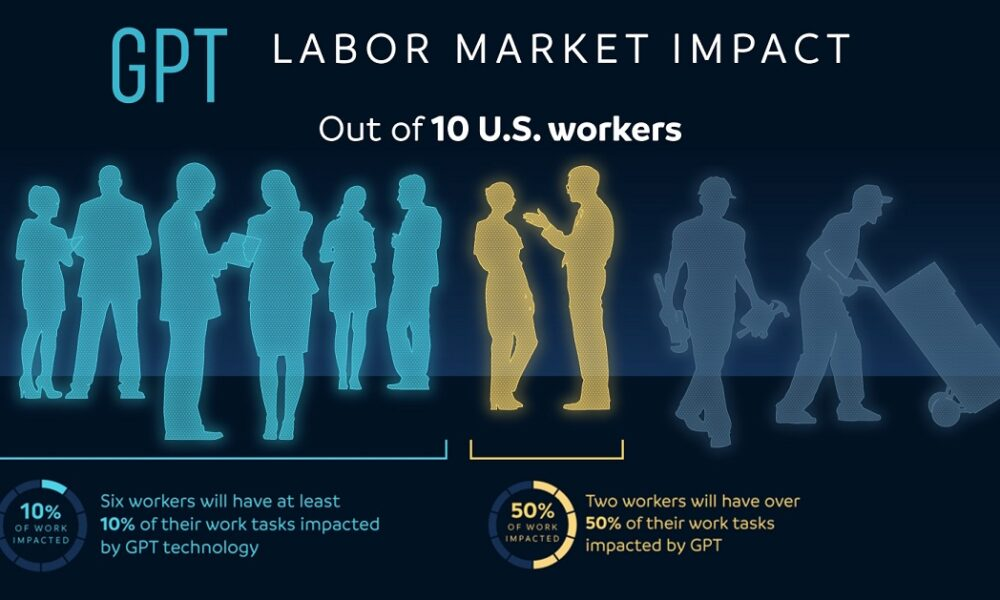
AI and the labor market are rapidly evolving concepts that are critical for understanding the future landscape of employment. As artificial intelligence technologies advance, they increasingly impact the workforce, prompting crucial discussions about the impact of AI on jobs. This technological disruption in labor is resulting in significant occupational churn, redefining roles and expectations across numerous industries. Economists are observing trends that suggest an accelerated shift towards an AI-driven workforce, indicating a transformation in the future of work with AI. With over a century of data revealing how technology has reshaped jobs, it is clear that embracing AI’s potential is imperative for both workers and employers alike.
The integration of advanced technology into various sectors marks a significant shift in employment dynamics and worker roles. As we navigate this wave of automation, the concept of technological change in the workforce becomes paramount. The disruption brought on by innovations like artificial intelligence is not only reshaping job descriptions but also influencing the demand for certain skill sets. With increased investment in AI and its capabilities, understanding how these workforce shifts manifest is essential for preparing for future challenges. In the realm of tomorrow’s jobs, adaptability and continuous learning will be vital for success in an ever-evolving employment landscape.
Impact of AI on Jobs: A Historical Perspective
The evolution of artificial intelligence in the labor market has sparked a significant transformation in job structures, akin to prior technological revolutions. Renowned economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers illustrate in their research how AI is driving current trends of occupational churn, echoing over a century of technological disruptions. From a historical standpoint, the analysis indicates notable stability in job types from 1990 to 2017. However, the recent influx of AI technology has triggered critical shifts, marking the sovereignty of knowledge-based roles. The study reveals that industries previously experiencing job polarization are now witnessing an undeniable tilt—favoring high-skill positions amidst decreasing opportunities in manual and low-paid roles.
These shifts can be seen as a double-edged sword. On one hand, job growth in sectors like STEM reflects a necessary evolution toward enhanced skills and training. From 2010 to 2024, positions within science, technology, engineering, and math have increased significantly, indicating that AI not only disrupts but also creates new opportunities. Conversely, this amplification of high-skilled roles signals an impending challenge for workers trapped in lower-skilled positions. As AI integrates deeper within workplaces, the demand for adaptability has never been more pressing. It compels individuals across various sectors to refine their capabilities to sustain their employment amidst this advanced competence race.
AI Workforce Changes and Their Implications
AI is redefining the landscape of work as it automates a plethora of routine tasks, prompting not only job losses but also considerable changes within existing roles. The recent findings highlight a stark decline in low-paid occupations, particularly in sectors like retail, where a 25% reduction in sales jobs has been recorded from 2013 to 2023. This shift underscores the reality that while AI catalyzes productivity, it concurrently decimates job availability in lower-end jobs, posing a serious risk to economic stability for untrained workers. The rapid adoption of predictive models and automation in e-commerce offers a glimpse into how technology is reshaping workers’ experiences and expectations in the workplace.
The reconfiguration of the job market can also create gaps in workforce readiness, necessitating strategic responses from both employees and policymakers. Demand for highly skilled individuals claims a larger share of the employment landscape, increasing pressure on less skilled workers. The transitional phase could lead to short-term productivity gains, but also raises concerns about long-term employment stability, especially for individuals whose roles are increasingly sidelined by AI’s capabilities. As AI’s base benefits filter through industries, there is a clarion call for reskilling initiatives and awareness programs to avoid a future workforce unequipped to meet new challenges.
Technological Disruption in Labor: Understanding Labor Market Volatility
The dimension of labor market volatility has seen significant fluctuations over the past century, especially with the advent of general-purpose technologies, as explored in the work of Deming and Summers. Notably, the 1950s to the 1980s experienced a surge in disruptions due to innovations that reshaped the employment landscape dramatically. These changes highlight the critical role AI plays in creating cyclical patterns of employment where uprooting established career paths becomes frequent. The historical perspective reveals that whereas technology once disrupted sectors, the advent of AI today threatens to overturn entire job categories, which were once considered stable.
Understanding the nuances of technological disruption in labor requires an examination of the factors driving these changes. Economic analyses show that advancements in AI do more than just render specific tasks obsolete; they redefine the essence of what jobs exist. This leads to a domino effect, where the investment in AI technologies alters the hiring patterns and skill requirements radically. Workers must navigate this landscape with adaptability, emphasizing continuous learning and the necessity of acquiring new skills to thrive in an environment characterized by rapid technological evolution.
Navigating the Future of Work with AI: Strategies for Resilience
As the labor market faces technological disruption, it is crucial for both workers and organizations to strategize for resilience in an AI-driven landscape. The symbiotic relationship between advancements in artificial intelligence and the labor force mandates businesses to adapt swiftly by investing in human capital. Organizations are increasingly focusing on upskilling their workers, ensuring they possess the necessary tools and knowledge to collaborate effectively with AI systems. By providing training programs tailored to emerging technologies, companies not only enhance workforce capability but also secure a competitive edge in their industries.
On the part of the workers, embracing a mindset committed to lifelong learning is essential. Engaging in continuous skill development will enable individuals to better navigate AI-induced changes, ensuring they remain relevant amid evolving job requirements. Workers must proactively seek training opportunities in technology-related fields and acquire skills that complement AI, such as creativity, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence—qualities that machines cannot replicate. Ultimately, the future of work with AI lies in a collaborative landscape where human ingenuity and technological advancements together pave the way for innovative solutions.
Occupational Churn: The New Norm in an AI-Dominated Environment
Occupational churn describes the rate at which job positions evolve within the labor market. The influence of AI on occupational churn underscores a shift that is becoming the norm rather than the exception as the U.S. labor market continues to undergo rapid change. Deming and Summers’ findings indicate an observed increase in churn since 2019, hinting that AI is fostering a new dynamic in which roles are not only replaced but also transformed, leading to a greater diversification of job types. While traditional job categories diminish, new roles emerge that emphasize higher cognitive skills and technical competencies.
Understanding occupational churn is imperative for both job seekers and employers as it reflects the shifting nature of skills and job availability. For employees, it presents an urgent necessity to adapt to these changes by developing competencies that align with the predicted demands of the job market. Employers, on the other hand, are tasked with creating a culture that embraces change and supports employee transition into new roles. Navigating the realities of occupational churn amid AI integration will define the workforce’s future, compelling all stakeholders to engage in a proactive approach and seek avenues for professional growth.
Automation Anxiety: Addressing the Fears of Job Displacement
As AI technologies advance, concerns about job displacement loom large, with ‘automation anxiety’ becoming a significant phenomenon in today’s workforce. The study highlights that a notable portion of workers remains fearful of being replaced by machines, which is exacerbated by statistics suggesting that 47% of U.S. occupations could be at risk due to automation. While these numbers might seem alarming, it is crucial to recognize the transformative potential of AI to augment rather than completely eliminate jobs. In many instances, AI tools are designed to relieve workers of tedious tasks, thus allowing them to focus on higher-level responsibilities that require human judgement and creativity.
Addressing the fears surrounding automation requires a robust dialogue about the role of AI in current and future job markets. Organizations have a responsibility to reassure their employees about the importance of workforce adaptability. Not only should they invest in innovative technologies, but they must also provide a framework for workers to understand how these technologies complement their roles rather than replace them. Empowering employees with education regarding the benefits of AI can foster a culture of collaboration, alleviating automation anxiety and strengthening the workforce’s ability to thrive alongside technological advancements.
The Role of Reskilling in an AI-Driven Economy
In light of the transformative shifts brought on by AI, reskilling emerges as a pivotal strategy for both individuals and organizations aiming to thrive in the evolving job market. As highlighted in the research, investments in AI are altering the job distribution, necessitating workforce transitions toward more advanced capabilities. By embracing reskilling initiatives, workers can reposition themselves within their industries, ensuring they are equipped with the competencies needed to operate effectively in increasingly automated environments. This proactive approach not only safeguards jobs but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and competitiveness.
Additionally, range and diversity in training programs are critical to addressing the varying speed at which industries adapt to AI. Tailored reskilling opportunities that account for the specific demands of different sectors can empower workers to transition smoothly into new roles. It is essential for organizations to focus on fostering a supportive environment where learning and adaptability are encouraged—facilitating a workforce that is not only agile but also prepared for future challenges presented by advancements in technology. Reskilled employees will be better positioned to not only remain employable but also contribute to an innovation-driven economy.
Lessons Learned from the Past: Preparing for Future Technological Disruptions
The historical analysis of labor market disruptions over the past century provides valuable lessons for confronting future challenges posed by AI technologies. Previous technological waves, including the introduction of computers and the internet, resulted in substantial shifts, often leading to temporary dislocation of workers before new opportunities surfaced. The current landscape calls for a similar understanding by policymakers and labor organizations to implement measures that can cushion the impact on affected workers, ensuring that disruptions lead to constructive rather than destructive outcomes. These strategies should include strong support systems for those in transition, ongoing education, and enhanced access to job markets.
Moreover, drawing from past experiences underscores the importance of a collaborative approach between governments, industries, and educational institutions. As AI technologies advance, fostering a culture of innovation will be essential for ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned in preparing for inevitable changes. By analyzing previous disruptions, stakeholders can formulate proactive policies to enable workforce resilience and adaptability, ultimately positioning them to not only survive but thrive amidst continual technological evolution.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI already impacting the labor market?
AI is significantly impacting the labor market by inducing technological disruption that transforms job roles and skills requirements. According to a study by economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers, recent trends indicate that AI is reshaping occupational churn, leading to increased demand for high-skilled jobs, particularly in STEM fields, and a decline in low-paid service jobs. As companies adopt AI technologies, job distributions within the economy are changing, requiring workers to adapt or reskill.
What are the trends of technological disruption in labor driven by AI?
The study identifies four key trends of technological disruption in labor due to AI: 1) Cessation of job polarization, favoring high-paid positions; 2) Growth in STEM jobs, which rose significantly from 2010 to 2024; 3) Decrease in low-paid service jobs, revealing stagnant employment; 4) Reduction of retail sales jobs, driven by technology and the rise of e-commerce. These trends highlight how AI is reshaping the future of work.
Is occupational churn increasing due to AI in the workforce?
Yes, occupational churn is increasing in the workforce partly due to AI. While a period of stability existed from 1990 to 2017, the data shows significant changes from 2019 onward, with AI fostering the growth of high-skilled jobs and causing a decline in certain sectors like low-paid service and retail positions. This trend illustrates how AI is transforming job markets rapidly.
What does the future of work with AI look like for employees?
The future of work with AI suggests a landscape where high-skill and STEM jobs will dominate, while roles requiring lower skill levels may diminish. Employees will need to adapt, acquiring new skills that complement AI technologies. As companies increasingly rely on AI, productivity demand will rise, pushing knowledge workers to enhance their efficiency in utilizing these advancements.
How does AI contribute to workforce changes and job displacement?
AI contributes to workforce changes by streamlining operations and automating tasks traditionally performed by humans, leading to potential job displacement. While it fosters short-term productivity increases, the long-term implications indicate that workers, particularly in lower-skill jobs, may face unemployment as their roles become less relevant. Research points to a significant shift in job distribution, emphasizing the importance of reskilling for affected workers.
What role does investment in AI play in labor market transformation?
Investment in AI plays a crucial role in transforming the labor market by altering job distribution. Companies are increasingly hiring technical talent and investing in frontier technologies, which has led to job growth in high-skill areas. This investment catalyzes technological disruption, reshaping occupations and the demand for skilled labor, further highlighting the need for workers to adapt to new roles created by AI innovations.
What are the potential benefits and risks of AI in the labor market?
The potential benefits of AI in the labor market include increased productivity, the creation of new high-skill jobs, and the emergence of innovative industries. However, the risks involve job displacement, particularly for roles that can be automated, and the need for workers to increasingly adapt their skillsets. The balance between these benefits and risks will shape the labor market’s landscape.
How can workers prepare for changes in the labor market due to AI?
Workers can prepare for changes in the labor market due to AI by embracing lifelong learning and engaging in upskilling and reskilling initiatives. Focusing on acquiring technical skills, particularly in STEM fields, can enhance employability in the evolving job landscape. Additionally, staying informed about AI developments and industry trends will enable workers to anticipate job market demands.
| Key Trends | Description | Implication | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Polarization Cessation | Slowdown in the growth of low-paid jobs, instead favoring well-compensated, high-skilled jobs. | Increases in high-paid positions can lead to economic improvements but may also heighten wage disparities. | |
| Surge in STEM Jobs | Significant increase in the share of STEM jobs from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024. | Rising demand for STEM skills may widen the gap between high-skilled workers and others. | |
| Decline in Low-Paid Service Jobs | Stagnation or decline of low-paid positions, especially in service sectors due to several factors including AI. | Potential loss of jobs may lead to increased unemployment levels and economic strains on vulnerable populations. | |
| Reduction in Retail Sales Jobs | 25% reduction in retail sales jobs, with e-commerce growing significantly post-pandemic due to technology adoption. | Accelerated shift towards online shopping may diminish traditional retail roles. | |
Summary
AI and the Labor Market are undergoing a critical transformation as evidenced by recent research from Harvard economists. This study highlights that artificial intelligence is not just a passing trend, but a revolutionary force reshaping job distribution across various industries. As job polarization decreases and STEM job growth accelerates, there is a clear shift towards high-paid positions. Additionally, the decline in low-paid service and retail jobs underscores the urgent need for workers to adapt to this evolving landscape. Understanding these dynamics is essential for workforce planning and policy-making in the face of technological advancements.